Credit: The credit equivalence of the Doctor of Medicine Program is 224 credits.
Study Plan of MD Program
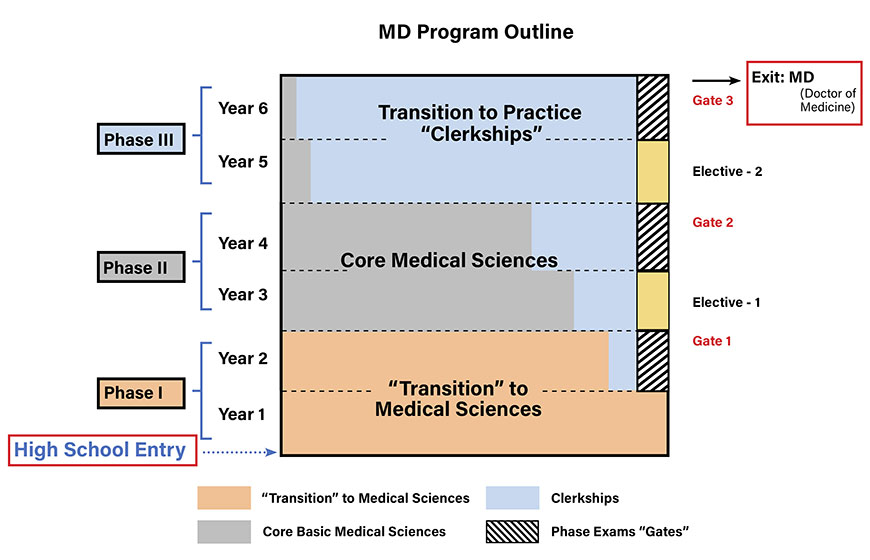
Phase I (Transition to Medical Sciences)
Year 1

Year 2

*General Education Courses
Credit Hour calculation: 1 Credit = 1 hour of Lecture/week for 15 weeks or 2 hours of Lab or Activity/week for 15 weeks
NOTE: There will be no prerequisite for any of the courses of year 1 and 2
Phase II (Core Medical Sciences)
Year 3

Year 4

*General Education Course; ^Parallel courses in the semester; $Number varies based on the selection of Elective-1 course
CC: Course Continued
# Work-Based Learning: 90 clinical contact hours to be completed during year 4 of the program
Elective-1: Each student opts for only one course, and it’s to be completed during year 4 of the program
Credit Hour calculation: 1 Credit = 1 hour of Lecture/week or 2 hours of Lab or Activity (PBL, VPL, Seminar, etc.)/week or 3-4 hours of clinical posting/week for 15 weeks.
Phase III (Transition to Practice or Clerkships)
Year 5

Year 6

*General Education Course; ^Parallel courses in the semester.
Credit Hour calculation: 1 Credit = 1 hour of Lecture/week or 2 hours of Lab or Activity (PBL, VPL, Seminar, etc.) / week or 3 hours of clinical posting/week for 15 weeks
Summary


Course Description
General Education Courses
GE Courses offered in Phase I:
CSE 102 Communication Skills in English
The overall aim of the course is to enable the student to become oriented to the communication tasks of a physician by developing an appreciation of the interpersonal nature of medical encounters in different clinical situations, develop basic communication skills and learn communication strategies. The course provides a variety of patient encounter settings to understand the basic interpersonal communication processes, gain sensitivity to patient perspectives and to develop a sense of personal awareness which will help the student deal with patients of all ages and both genders in routine and challenging situations and, work effectively as a member of the healthcare team.
ITH 101 Information Technology for Healthcare Professionals
This course provides the essential principles and basic knowledge on technology sciences for Healthcare Professionals necessary for their day-to-day practice in the world of digital health. In addition, the course will provide concepts that connect applications in developing practical skills for accessing and using the information to deliver quality patient care, use education technology and develop electronic communication skills.
MEL 101 Medical Education and Lifelong Learning
This student-centered course provides students with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to become independent lifelong learners through the continuum of undergraduate education, postgraduate education and continuing professional development. This course will enable the students to understand the competencies of a medical doctor and their relation to the teaching and learning activities. Students will learn to work in small groups through problem-based learning (PBL) and Team-Based Learning (TBL) sessions. This course will help students understand how to develop their portfolio and use it to reflect and guide their lifelong learning. They will learn how to construct concept maps and study plans, which will help them learn better. They will learn to perform a literature search that will help them practice evidence-based medicine. Understanding the principles of assessments will allow them to guide learning. In principle, this course will help students acquire lifelong learning and leadership skills.
BSE 101 Behavioral Science and Ethics
The course is designed to give an overview of the main topics in Behavioral Sciences and Ethics including biological basis of behavior, mental processes, sensation and perception, learning, motivation, intelligence, human development, personality, socialization, social groups, changes in trends, problems of determined individuals and universal ethical principles. The objective of the course is to enable the student to understand and apply the knowledge, skills and attitude developed in this course to communicate effectively. Students will learn and practice strong values, ethical conduct and social responsibilities, especially personal, academic, and professional integrity while developing collaboration in diverse team settings. Students will be trained to display sensitivity to cultural, psychosocial, and ethical issues.
Emirati Studies (EMS 101)
This course provides an in-depth exploration of the most significant aspects of the United Arab Emirates, offering students insights into the features of Emirati society. It covers economic and social development, affirming the nation’s core values and heritage, and includes studies in key areas such as history, geography, internal and external policies, social systems, human development, and demographics. The course emphasizes the role of Emirati citizens in development, with particular attention to women’s empowerment and their societal contributions. Additionally, it highlights the country’s focus on sustainable energy, economic advancements, and development indicators, alongside its global competitiveness.
Furthermore, the course addresses future strategic development plans and the challenges they entail, recognizing the UAE’s pioneering role on the international stage and its progress in global development and competitiveness indicators. It offers a detailed analysis of the social aspects of Emirati society, focusing on its unique culture, community dynamics, and the interplay of multiethnicity and cultural diversity, underpinned by the values of tolerance and indigenous traditions. By the end of the course, students will have developed an awareness of multiculturalism and the ability to relate their understanding to a global context.
GE Courses offered in Phase II
HSS 101 Health Systems
The Health Systems Science course examines global healthcare delivery systems, emphasizing organizational dynamics to optimize patient care and efficiency. It integrates health systems science with clinical practice, focusing on entrepreneurship, innovation, and sustainability in healthcare management. Students develop leadership skills, address global health challenges, and explore health economics principles. The course encourages applying systems thinking to design, evaluate, and implement health interventions and policies, promoting health equity and improving outcomes. Through hands-on exercises, students learn to develop sustainable solutions and craft effective business plans for modern healthcare challenges.
AIH 101 Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare Professionals
Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare Professions is an intermediate level course which falls under the Technology Sciences domain for healthcare professionals. The course examines the evolution of AI, the conceptual development of AI techniques, such as machine learning, deep learning, data sciences, and comprehensively covers data security, privacy, as well as the social and legal implications of AI in healthcare. The learner will explore the benefits of AI’s application in healthcare – which will prepare future health practitioners to successfully collaborate with AI and data science experts in an immersive AI-based healthcare environment.
GE Courses offered in Phase III
HIS 101 Health Information System
This course prepares the student to utilize informatics and healthcare technologies in the healthcare of individuals for the enhancement of patient outcomes as well as to gain an appreciation of the proficiencies required of an expert knowledge worker and apply these competencies to routine practice as a Healthcare professional.
The course focuses on advanced topics such as data analytics and cybersecurity in healthcare. This final phase prepares students to manage and utilize complex health data, a critical skill in today’s data-driven healthcare environment.
The course is enriched with technology and data science and has an objective to substantially raise the clinical acumen of its graduates, equipping them with the digital literacy imperative in the contemporary realm of medical practice. The course objective is to close a significant educational gap, aligning medical training with the technological exigencies of today’s healthcare landscape.
Phase I MD Program Core Courses
ANA 201 Anatomy 1
This course is designed to introduce medical terminology, general histology and the basics of human embryogenesis for students, outlining the sequence of developmental events in a typical embryo. It also provides the student with concepts related to the gross structures of upper and lower extremities including their development. Laboratory sessions will help students practice safety measures and learn ethical values regarding cadavers, promoting teamwork and lifelong learning. This course will enable further understanding of organ-system courses in Phase II.
PHY 201 Physiology 1
This course is designed to study the function of the normal body and integrates all aspects of the individual cells and organs of the human body. The contents of the course will focus on three areas based on disease-health continuum, namely normal functioning of human body systems, control of body functions and pathophysiology or alterations in body function. The objective of this course is to enable the student to explain the function of body using biophysical principles, nerve and muscle functions, homeostasis, and organ-system level of hematopoietic system. Students will be able to apply the physiological principles to perform experiments to record basic physiological parameters and interpret the clinical data during the organ-system courses in Phase II.
BCH 201 Biochemistry 1
This course is designed to provide understanding of the physical-chemical properties, structure-function relationships, and clinical relevance of biomolecules including specialized proteins and mechanism of enzyme action. Biochemical calculations learned in this course will lay the foundation for laboratory data interpretation. Laboratory sessions for identification of biomolecules by chemical methods, their separation by electrophoresis and chromatography will help understand principles of various analytical techniques. The course lays a strong foundation for understanding the basics of ‘metabolism and nutrition’ and the manifestations of molecular defects covered in the subsequent courses of the program.
CGE 201 Cell Biology and Genetics
This basic course in cell biology and genetics has been introduced as part of modern medical education with the purpose of enabling the medical students master the structure and functions of cellular components, genetic processes, structure-function relationships of biomolecules and bio-membranes with an emphasis on their clinical relevance. An insight into the genetic basis of disorders forms a strong foundation in understanding the diagnosis and management plan of those genetic disorders and importance of genetic counseling. Laboratory sessions help in identifying cells and stages of cell cycle using microscopy and pedigree analysis using charts. This knowledge will provide a solid foundation for a better understanding of human health as well as studying other related organ-system courses.
ANA 202 Anatomy 2
This course is designed to obtain a deeper knowledge of the gross structure of the organs in the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis and its relations to each other. The theoretical knowledge is supplemented with cadaveric demonstrations. It also introduces students to the concept of “living anatomy” to visualize the structure of the thorax and abdomen on conventional medical imaging and on a living human body. Laboratory sessions will help students practice safety measures and learn ethical values regarding prosected specimens, promoting teamwork and lifelong learning. This course will enable further understanding of organ-system courses in Phase II.
PHY 202 Physiology 2
This course is designed to study the organization and function of the Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Alimentary and Urinary systems. It integrates all aspects of the individual cells and organs of the human body. The contents of the course will focus on three areas based on disease-health continuum namely normal functioning of human body systems, control of body functions and pathophysiology or alterations in body function. This course would provide the basis to explain the pathophysiological aspects of altered health to be learnt in later courses.
BCH 202 Biochemistry 2
This course builds on the normal structure and function of the biomolecules learned in Biochemistry 1 and focuses on the metabolism of biomolecules and associated disorders. It also emphasizes nutritional aspects of public health, including nutrition-related disorders, nutritional support for hospitalized patients, food toxicity, and safety. Laboratory sessions for quantitative analysis of common biochemical parameters provides an opportunity to practice universal safety precautions, and related skills sessions help understand ethical values concerning human subjects and will promote teamwork and lifelong learning. This course will enable understanding of disease manifestations due to molecular defects during organ-system courses in Phase II.
PUH 201 Public Health 1
This course in Public Health allows the students to learn concepts of health and health-related events. It emphasizes personal, social, economic, biological, and behavioral determinants causing the disease among different population groups. It will also focus on the concepts of disease progression, levels of prevention, and strategies to improve the health status of a population. The epidemiology of communicable and non-communicable diseases, screening methods and their challenges, and related ethical approaches will be covered. The fundamental knowledge gained in this course will help the student to understand the risk factors for disease and the application of appropriate preventive strategies during their clinical years.
ANA 203 Anatomy 3
This course emphasizes providing the student with fundamentals of the gross and microscopic appearance of the structures pertaining to the head and neck and their relation to each other. It will also highlight the detailed structure of both central and peripheral nervous systems and how both systems are harmoniously integrated concerning their function. This course introduces the “live anatomy of the head and neck” as depicted in medical imaging in a living body. Students will be able to describe the significant characteristics of the cranium, neck, face, temporal, and infratemporal regions.
PHY 203 Physiology 3
This course is designed to study functions of the normal body and integrate all aspects of individual cells and organs of the human body. The contents of the course will focus on three areas based on the disease health continuum, namely, the normal functioning of human body systems, control of body functions, and pathophysiology or alterations in body function. The objective of this course is to enable the students to explain the functions of major hormones and their regulation, the role of the sensory and motor systems, special sense organs, limbic systems, and neurophysiological aspects of sleep, learning, and memory.
MOB 201 Molecular Biology
The Molecular Biology course provides the students with a good foundation in concepts of molecular biology including techniques and applications. The course starts by introducing students to the structure and function of nucleic acids, organization of the genome, processes of replication, concepts of repair, RNA and protein synthesis, then moves on to mechanisms of gene expression and regulation, and finally to the basics of DNA technology. Genetically-modified organisms and genome analysis are also touched upon.
REM 201 Research Methodology
The course encourages and empowers new investigators to conduct their original research projects. It provides a practical step-by-step guide to conducting quantitative and qualitative research in medicine. This course covers the entire research process, from formulating a study question and selecting a study approach to collecting and analyzing data and disseminating the findings. The course shows students how they can contribute to improving the health of individuals and communities through research. The course also emphasizes the importance of critical appraisal skills, enabling students to evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in current knowledge.
BIS 201 Biostatistics
This course presents biostatistics related to health and medical problem-solving in an analytical way. This course introduces the student to the principles of statistics and the concept of clinical trial design and analysis. Students will be able to explain the concepts of variables, data description, probability, and descriptive and inferential statistics, as well as demonstrate basic knowledge of application data analyses in applied health sciences. Students will be able to make decisions about the appropriate use of descriptive and inferential statistics according to the type of data and study design for answering a particular research question. This is the foundation and prerequisite for courses that will be taken later on, such as research and evidence-based medicine.
PUH 202 Public Health 2
This course provides an overview of environmental health, occupational health, and health systems and organizations. There is a focus on the impact of exposure to a range of environmental and occupational, physical, chemical, biological, and psychological factors on the individual’s and population’s health. The students will distinguish the relevance of environmental sustainability and eco-friendliness to combat climatic changes and maintain resources for coming generations. The course will explore global environmental health issues like air and water pollution, waste management, disaster, and global warming. The course covers principles of prevention and control of environmental and occupational hazards, accidents, work-related illnesses, and disorders. The course will also introduce health system models, delivery of health services with an emphasis on primary healthcare services, and the role of national and international organizations in controlling the spread of diseases and maintaining health.
GMI 201 General Microbiology
This course provides an understanding of pathogenic microorganisms and the mechanisms by which they cause diseases in the human body. During this course the students will learn the principles of aseptic techniques, the role of the human body’s normal microflora and concepts of infectious disease transmission and prevention. It provides an opportunity to develop basic skills in interpreting laboratory findings of microbiological tests. The course lays a strong foundation in understanding the basics of pathophysiology and prevention of infectious diseases which are covered during the organ-system courses in Phase II and during the clerkship phase.
GPH 201 General Pharmacology
This course provides a foundation by describing the various changes that the drug undergoes after administration into the body. Mechanisms by which cells, tissues, and organs sense and respond to their environment are presented, along with pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, including the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of pharmacologically active compounds. The site of action, routes of drug administration, mechanism of action, and the multiple effects of various therapeutic agents through receptor and non-receptor mechanisms are also discussed. The course also emphasizes the general principles of antimicrobial therapy and chemotherapy, new drug discovery, prescription writing, and the drugs acting on the autonomic nervous system. This course prepares the students by offering the knowledge required for understanding the actions of drugs on various organ-systems in the subsequent organ-system based courses of Phase II.
GPA 201 General Pathology
General Pathology deals with the study of mechanisms of cell injury and principles of tissue responses to various abnormal stimuli, including disturbances in hemodynamics from the molecular level to the effects on tissues and organs that form the basis of disease. The course builds on the foundational knowledge of biomolecules, molecular genetics, normal structure and functions of cells, tissues and organs, and organ-systems of the human body. General pathological concepts and principles will be applied to specific organ-system courses to understand the common disease processes affecting each system with respect to the causes, mechanisms, and structural and functional alterations that underlie clinical manifestations of disorders.
IMU 201 Immunology
The course deals with the structure and functions of the immune system and the mechanism of the innate and adaptive immune response. It also emphasizes the knowledge of immune response to microbes, immune-prophylaxis, failures of the immune system, hypersensitivity, role of MHC in the transplantation, tumor immunogenicity and microenvironment, and immunotherapy. Laboratory sessions for the quantitative determination of common immunological parameters provide an opportunity to practice universal safety precautions and promote teamwork. This course will help the student to have a strong foundation regarding the basic principles involved in immunology, which in turn will help them to understand the concepts involved in clinical immunology, medical microbiology, and immunopathology in the subsequent courses taken in the preclinical and clinical years.
Phase II MD Program
BIS 301 Blood and Immune System
The contents of the Blood and Immune System course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention, and management of common disorders of the Blood and Immune system using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learnt in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitutes the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
RES 301 Respiratory System
The contents of the Respiratory System course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention and management of common disorders of the Respiratory System using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learnt in Phase I. Problem-Based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitutes the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
CVS 301 Cardiovascular System
The contents of the Cardiovascular System course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention and management of common disorders of the Cardiovascular System using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learned in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitute the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
REP 301 Research Project
This course running over 3 semesters provides students the opportunity to conduct quality research under faculty guidance. Students will develop a research proposal in the third year [semester 5], collect and analyze the data in semester 6 of the same year, and present the research findings in fourth year [semester 7]. This will enable students to integrate the knowledge, skills, and competencies acquired in Research Methodology and Biostatistics courses in year 2 with the clinical knowledge and skills to conduct research in the community or in an institutional setting. The students will develop the needed research competency to collect, analyze, interpret, and present data, taking into consideration all ethical and legal requirements. The course will enable students to apply critical thinking, communication, and analytic skills during various steps of research. An online certificate on ‘Research Ethics and Good Clinical Practice’ must be obtained before starting the study.
ALS 301 Alimentary System
The contents of the Alimentary System course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention, and management of common disorders of the Alimentary System using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learnt in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitutes the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
URS 301 Urinary System
The contents of the Urinary System course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention, and management of common disorders of the Urinary System using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learned in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitute the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
EDB 301 Endocrine System and Breasts
The contents of the Endocrine System and Breasts course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention and management of common disorders of the Endocrine System and Breasts using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learnt in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitutes the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
RPS 301 Reproductive System
The contents of the Reproductive System course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention and management of common disorders of the Reproductive System using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learned in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitute the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
MSS 301 Musculoskeletal System and Skin
The contents of the Musculoskeletal System and Skin course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, and principles of prevention and management of common disorders of the Musculoskeletal System and Skin using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learned in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitute the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
NES 301 Nervous System
The contents of the Nervous System course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems/presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. This course focuses on the etiology, pathophysiology, investigations, behavioral and ethical aspects, principles of prevention, and management of common disorders of the Nervous system using a multidisciplinary integrated approach. The course builds on the previous knowledge of normal structure, function, and general pathology mechanisms of disease learnt in Phase I. Problem-based Learning and Virtual-Patient Learning using high-fidelity Artificial Intelligence-based simulated patients constitutes the primary strategy of learning and teaching. Students also learn common clinical skills related to the system and interpret the results of investigations in clinical skills sessions to prepare them for the clerkship phase.
IMS 301 Integrated Multisystem Course
The contents of the Integrated Multisystem course form the ‘core knowledge for practice’ in which prevalent and important clinical problems / presentations in the community are identified through a patient-centered approach. The integrated multisystem course offers opportunities to integrate between and beyond the organ systems. The course will be structured around a series of cases which are multisystem in nature using Virtual-Patient Learning and Problem-Based Learning. The students will learn how to present case studies by following an evidence-based approach, helping them to acquire critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It will also offer opportunities to review and reinforce concepts learnt in individual organ-systems to prepare them for the Phase II exit examination and to be engaged in Phase III “transition to practice”.
WBL 301 Work Based Learning
The module is offered as 90 contact hours of clinical postings at designated clinical posting sites. The Work-based Learning course provides excellent opportunities for students to apply and perform skills like history taking and physical examination learned in the simulated setting (during the skills sessions in each organ-system course) on real patients under supervision and observe the clinicians interact with the patients in the ambulatory care and inpatient settings. They will also appreciate the role of teamwork in providing care for the patient and introduction to the different healthcare systems. This course prepares the students for a smooth transition to the clinical years.
CLT 301 Clinical Training (Elective-1)
Elective clinical posting serves to promote the application of professional skills in the practice of medicine in different healthcare systems, develop confidence, maturity, responsibility and interpersonal skills in novel settings, and demonstrate a greater understanding of ethical, confidential and sensitive issues when exposed to patients with different beliefs, values and culture. The students can opt for any specialty at any recognized site (teaching hospital) either within or outside the country. GMU has collaboration with several national and international universities and teaching hospitals to facilitate placement of students.
CAR 301 Cancer Research (Elective-1)
The course will focus on research that addresses important problems related to cancer. From molecular pathways to the experience of cancer survivors, this course offers a comprehensive exploration of advancements in cancer research. Through individual or collaborative projects, students will develop a profound understanding of the various research methodologies employed in cancer studies. The students will collect, analyze, and interpret data related to cancer under faculty supervision. The data can be epidemiological, clinical, social, behavioral, molecular, or educational. The students will communicate research results in written and verbal forms. The students have to provide a certificate for completing one of three online courses offered by Coursera on principles of cancer biology and diseases.
HPS 301 Health Psychology (Elective-1)
Health Psychology is a specialized area within the broader field of Psychology that investigates the influence of psychological and social elements on health and illness. This discipline encompasses the study and clinical management of the interconnected roles of cognition, behavior, emotions, and biological processes in relation to health. The objective of this course is to familiarize students with the principles of health psychology, covering fundamental biology, the interplay between biological and psychosocial factors, health-related matters, and psychological interventions aimed at influencing health outcomes. In essence, health psychology signifies a contemporary perspective in the realm of mind-body medicine.
HUM 301 Humanities in Medicine (Elective-1)
The course provides medical students with basic knowledge of how humanities in medicine are represented through the arts, philosophy, history, anthropology, psychology, and sociology. Students will understand the human response to disease, improve their empathetic abilities, and influence the way in which they practice medicine, manage their own emotions, and communicate with patients. By engaging students in creative work on medical themes, including activities like acting, drawing, writing poetry, and watching and discussing films, the course aims to hone students’ critical thinking skills, creative aptitudes, and emotional intelligence.
CLN 301 Clinical Nutrition (Elective-1)
This multidisciplinary elective course provides medical students with insights into the influence of nutritional status on the immune system and food-borne illnesses and the management of chronic diseases like diabetes mellitus, heart, liver, and kidney diseases, and cancer. It also focuses on the concept of food allergy, nutrigenomics, and nutrient interaction with drugs and medications in the body. It also helps in understanding the unique pediatric nutritional needs as well as the challenges, and interventions relevant to nutrition in the elderly and critically ill patients. Students will also gain an understanding of sports nutrition, weight management, and the complex interplay between psychological factors and dietary behaviors.
Phase III MD Program
Year 5
MED 401 Medicine 1
The clerkship in Medicine 1 in Year 5 is designed to give the student broad exposure to common medical conditions in clinical practice. The student will learn to take a relevant history, perform a general and focused systemic examination, formulate differential diagnoses, and develop a plan to manage common acute and chronic medical disorders in ambulatory and inpatient settings. This clerkship lays the foundation for the Medicine 2 clerkship in Year 6.
SUR 401 Surgery 1
The clerkship in Surgery 1 in Year 5 is designed to give the student broad exposure to the principles of diagnosis and management of common surgical problems, including surgical emergencies. It provides the students with adequate clinical encounters in ambulatory, bedside and OR settings. During the rotation, the student will be expected to focus on basic principles of peri-operative, operative, and postoperative management of the patient with a surgical problem. This clerkship lays the foundation for the clerkship in Surgery 2 clerkship in Year 6.
OBG 401 Obstetrics and Gynecology
The clerkship in Obstetrics and Gynecology is designed to give the student broad exposure to the principles of diagnosis and management of common gynecologic and obstetric conditions in ambulatory care, delivery rooms, operation rooms, and inpatient settings. Procedural skills like delivering a baby, taking a PAP smear, and pelvic assessment are also learned and practiced in the safe environment of the simulation lab.
PED 401 Pediatrics
The clerkship in Pediatrics is designed to give the student broad exposure to common pediatric conditions in ambulatory care, intensive care, and inpatient settings. During this clerkship, the student will assess the normal growth and development of a child, learn to obtain clinical history in an age-appropriate and sensitive manner from a child and or the accompanying adult, conduct a physical examination appropriate to the condition, and interpret the clinical findings. The student will be able to interpret lab results to suggest a diagnosis and discuss the management of the disease in the pediatric age group.
EYE 401 Ophthalmology
The clerkship in Ophthalmology is designed to give the student broad exposure to common ophthalmology conditions in ambulatory care, operative, and inpatient settings and indications for referring cases to ophthalmologists. The student will learn to take an ophthalmic history and perform a basic eye examination to detect common eye abnormalities, interpret clinical findings, arrive at a diagnosis, and discuss the management plan. The students will also observe ophthalmic investigative procedures and surgeries performed by the faculty.
ENT 401 Otorhinolaryngology
The clerkship in Otorhinolaryngology is designed to give the student broad exposure to common conditions in ambulatory care and operative and inpatient settings related to ear, nose, and throat diseases. The student will obtain a history and perform a basic head and neck examination with appropriate equipment. The students will discuss the clinical findings, diagnose common ENT problems, and design a treatment plan. The students will also observe common ENT surgeries performed by the faculty.
Year 6
MED 402 Medicine 2
Medicine 2 clerkship is built upon the knowledge and competencies gained in Medicine 1 clerkship in year 5. The students are rotated in medical sub-specialties like neurology, nephrology, dermatology, and cardiology. This clerkship is designed for medical students to gain additional experience in clinical presentation and management of medical conditions. This clerkship emphasizes integrated patient care, teamwork, and preparing the student for internship and professional practice.
SUR 402 Surgery 2
Surgery 2 clerkship is built upon the knowledge and competencies gained in Surgery 1 clerkship in year 5. The students are rotated in surgical subspecialties of Trauma and Acute care, Orthopedics and Urology. This clerkship is designed for medical students to acquire additional knowledge and skills to provide appropriate levels of care under supervision for commonly encountered surgical diseases. This clerkship emphasizes integrated patient care, teamwork, and preparing the student for internship and professional practice.
FAM 401 Family Medicine
This clerkship provides the learners with an insight into the continuing and comprehensive medical care for individuals and their families. It differs from other specialties because it encompasses all ages, genders, organ-systems, and every disease entity. The heart of this clerkship is the patient-physician relationship viewed in the context of the patient’s family. The students will spend most of their time in the primary care settings, where they will clerk patients and their families under the supervision of faculty.
EMR 401 Emergency Medicine
The emergency room rotation offers a special environment and an opportunity to practice fundamental skills of decision-making in an acute care setting. The aim of the posting is for the learner to develop critical thinking and multi-tasking skills in a busy ER facility, understand the concept of acute care and patient transfer, and develop good communication skills and professional interaction with the patients, relatives, and other medical personnel.
CCA 401 Critical Care and Anesthesia
The posting in the critical care areas of ICU and CCU is designed to provide the students with practical knowledge about the management of critically ill patients. Students get opportunities to improve their bedside clinical skills, including focused history taking, clinical examination, relevant investigations, and appropriate treatment relevant to the acute critically ill patient, master the essential emergency life support and resuscitation skills, and develop the habit of good communication skills and professional interaction with the patients and other medical personnel including breaking bad news. The anaesthesia clerkship will expose the students to basic principles of anaesthesia induction, maintenance, recovery, and postoperative care. This will also support the basic life support skills of the student.
PSY 401 Psychiatry
This clerkship will provide the medical student with experience in evaluating and treating patients with various mental illnesses. Students will be exposed to all age groups, including children, adolescents, adults, families, and geriatric patients, with an emphasis on understanding cultural issues in mental health. The clerkship will also stimulate a holistic thinking process in the medical student, initiating awareness of the biopsychosocial model of diseases in patients. The overall aim of the rotation is to give students a broad view of the spectrum of mental health problems.
ELE 401 Elective–2
Elective 2 posting in year 6 serves to promote the application of professional skills in the practice of medicine in different healthcare systems prior to graduation, develop confidence, maturity, responsibility, and interpersonal skills in novel settings, and demonstrate a greater understanding of ethical, confidential, and sensitive issues when exposed to patients with different beliefs, values, and culture. The student is encouraged to pursue the electives either in the country or abroad in any medical specialty, including research or healthcare management. GMU has collaboration with several national and international universities and teaching hospitals to facilitate placement of students.
QHC 401 Quality in Healthcare
This course prepares students to become strong advocates for quality care and patient safety in healthcare settings. It provides foundational knowledge of essential quality concepts necessary for healthcare professionals, focusing on recognizing patient safety goals, identifying risk management priorities, and understanding core quality improvement strategies.
The course integrates quality assurance, patient safety, accreditation, and clinical audits to meet an emerging demand for professionals with quality and patient safety knowledge who have the capacity and competence to grow and sustain a culture of continuous improvement at all levels of the healthcare delivery system. This course encourages a hands-on approach and completing a clinical audit or a quality improvement project as an expected outcome at the end of this course.